An Intelligent Tutoring System Aims to Improve Engineering Students’ Drawing Skills
May 13, 2021
 Julie Linsey, Director of the Innovation, Design Reasoning, Engineering Education and Methods Lab and Associate Professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering, recently received a collaborative research grant from the NSF Division of Undergraduate Education to improve undergraduate students’ ability to draw representations of structures and systems. Sketchtivity, an intelligent tutoring system that teaches engineering students how to draw will be used in this project to examine the impact of drawing instruction on student learning.
Julie Linsey, Director of the Innovation, Design Reasoning, Engineering Education and Methods Lab and Associate Professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering, recently received a collaborative research grant from the NSF Division of Undergraduate Education to improve undergraduate students’ ability to draw representations of structures and systems. Sketchtivity, an intelligent tutoring system that teaches engineering students how to draw will be used in this project to examine the impact of drawing instruction on student learning.
The project’s investigative team comprises Tracy Hammond and Vinayak Krishnamurthy from Texas A&M University, Julie Linsey and Wayne Li, Professor of Practice, Design and Engineering at Georgia Tech, Kerrie Douglas, assistant professor at in the Department of Engineering Education at Purdue, and Vimal Vishwanathan associate professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at San Jose University. The $1,500,000 total project titled, "Collaborative Research: Fostering Engineering Creativity and Communication through Immediate, Personalized Feedback on 2D-Perspective Drawing’" will be shared by Texas A&M University, Georgia Institute of Technology, Purdue University, and San Jose State University.
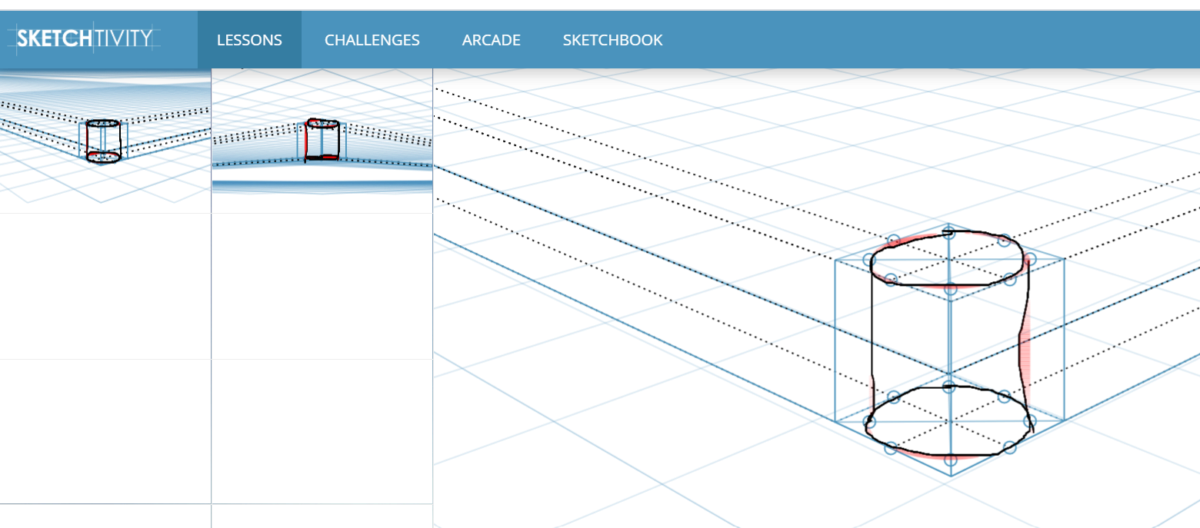
Sketchtivity provides real-time feedback on drawings made on a screen instead of paper. This application, developed by the research team, helps students with iterative, personalized feedback on the drawing and facilitates their overall learning experience. During the transition from hand drafting to Computer-Aided-Design, free-hand drawing and its associated benefits were unintentionally removed from the engineering curricula. This eventually resulted in a lack of proficiency by students and faculty when it came to free-hand drawing. This project will support reestablishing perspective drawing in the engineering curricula to meet the practical needs of students once they enter the workforce. This research is expected to have extensive significance in undergraduate STEM education.
Through this project, around 5,000 diverse undergraduate and graduate students at four partnering institutions would receive this Sketchtivity software. This would include a large percentage of women and students who are under-represented in the STEM field. The project aims to bring about crucial knowledge about drawing-based artificial intelligence (AI) tools and increase cognizance of the effects that feedback and reflective prompts have on drawing skills, learning and creativity. Assessments made by humans will be compared to AI-based assessments to provide supplementary information about the development of intelligent tutoring systems. The project will investigate the students’ drawing ability and how it is impacted by their creativity and spatial reasoning skills and whether it is transferable to other engineering courses.
In order to determine the project outcome, a mixed-methods approach that uses surveys, validated assessments for engineering design creativity, and drawing quizzes will be used. The NSF IUSE: EHR program seeks to improve the effectiveness of STEM education for all students, through research and development projects. The program supports the creation, exploration, and implementation of promising practices and tools, through the Engaged Student Learning Track.
